Creating a Stark key pair
StarkEx supports the following wallet types:
-
BIP32 compatible wallets, such as Ledger
-
Non-BIP32 wallets
StarkWare recommends two methods for creating a private Stark key, depending on the type of the wallet.
Deriving the public Stark key
You can use the StarkEx Crypto SDK to derive the key. Call the getPrivateKeyFromEthSignature function to generate the private key from the signature and then the privateToStarkKey function to compute the public Stark key.
BIP32 Compatible Wallets
BIP32 compatible wallets should implement EIP-2645. This EIP describes a path and a key derivation algorithm that uses this path to derive the private Stark key.
The path consists of four passed parameters and two internal parameters as described below, and has the following structure: m/purpose'/layer'/application'/ethAddress1'/ethAddress2'/index
Passed Parameters
purpose
|
|
layer
|
Differentiates between technologies, defined as |
application
|
Differentiates between applications, defined as |
index
|
Allows multiple keys per Ethereum address. |
Non-BIP32 Wallets
|
For security reasons, this method is not recommended when using any wallet that does not use a deterministic signing algorithm. For example, multi-party computation (MPC) wallets should not use this method. |
Deriving a Stark key proceeds as follows:
-
The user signs a message, using his Ethereum signature, such as by using MetaMask. It is recommended to use EIP-712 in order to provide transparency to the user when they are signing the message.
It is recommeneded to add a warning inside the message that the user should only sign the message if it was sent from a specific domain, as in Figure 1.
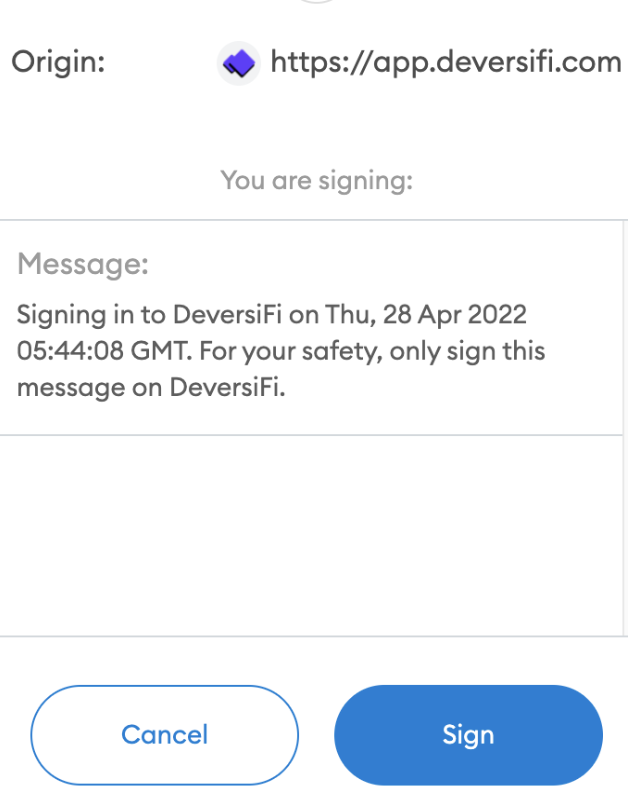 Figure 1. MetaMask pop-up. Prompts a user to sign using their Ethereum key in order to generate a private Stark key.
Figure 1. MetaMask pop-up. Prompts a user to sign using their Ethereum key in order to generate a private Stark key. -
The signature
(r,s,v)is used as an input to the grinding algorithm that outputs thestarkPrivateKey.